Enclosure Acoustics Practice
Acoustic / WinISDBack to Basics
Thanks to technological advancements, today's audio systems can achieve sound quality approaching that of traditional speakers, even in very compact sizes, by leveraging DSP and Class D amplifiers, along with more measurement methods and theoretical foundations.
However, as the Chinese proverb goes, 'reviewing the old enables one to understand the new.' By understanding how speakers achieved high fidelity through adjustments in driver characteristics and cabinet physical properties without the aid of these modern technologies, we can learn from past experiences in optimizing these physical conditions. This knowledge provides deeper insights and informs our design thinking for future acoustic product designs.
A Full-Range Bookshelf Speakers Build
As a starting point, we chose passive bookshelf speakers from a two-channel system as our research subject, each enclosure paired with a full-range driver to simplify design considerations such as the interaction between tweeters, woofers, and crossovers. We employed an inverted tube enclosure layout to enhance the bass volume sensation.
Thus, for these speakers, knowing the acoustic characteristics of the driver, we only needed to find the appropriate enclosure volume and dimensions of the inverted tubes to optimize the performance of the driver.
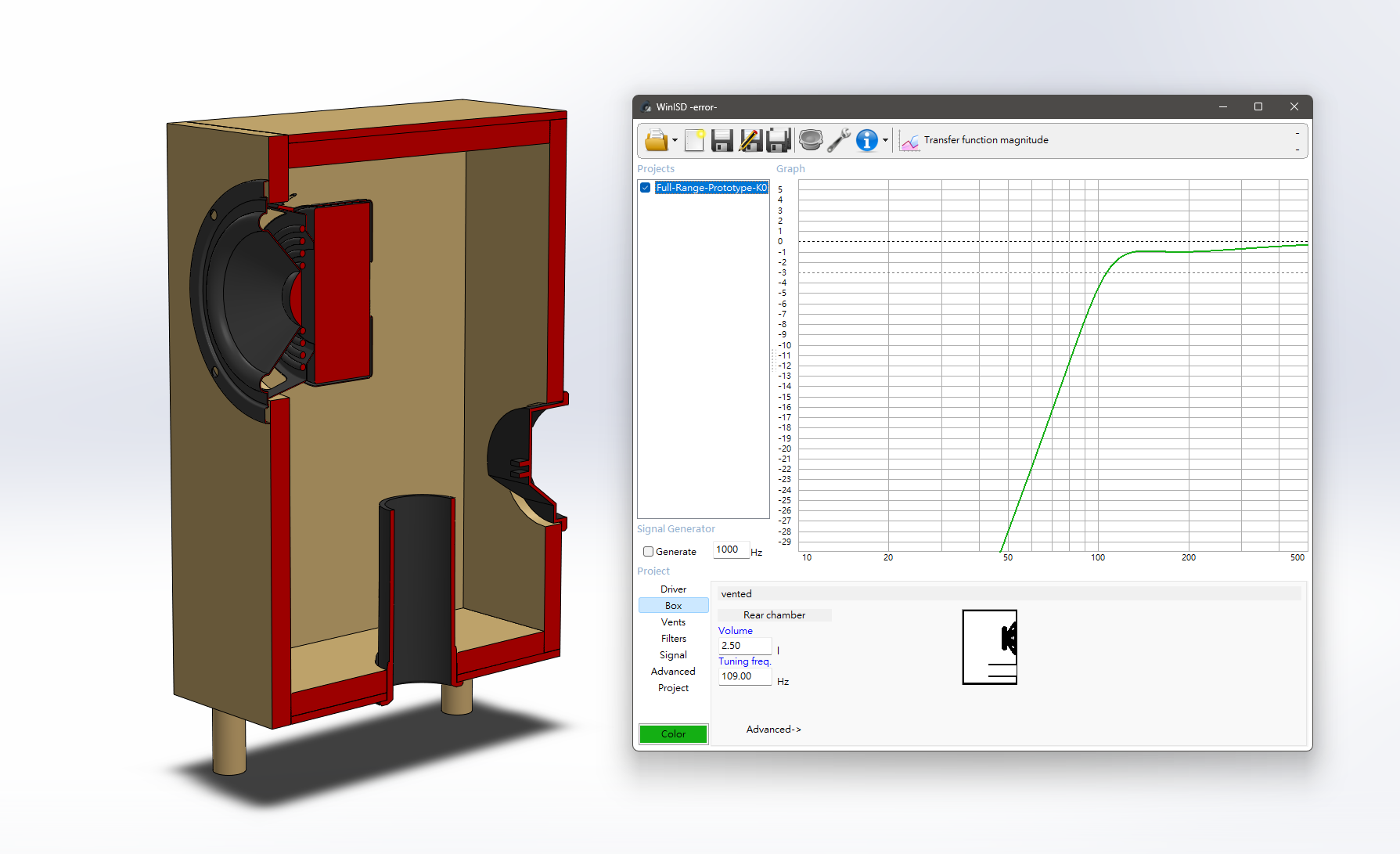
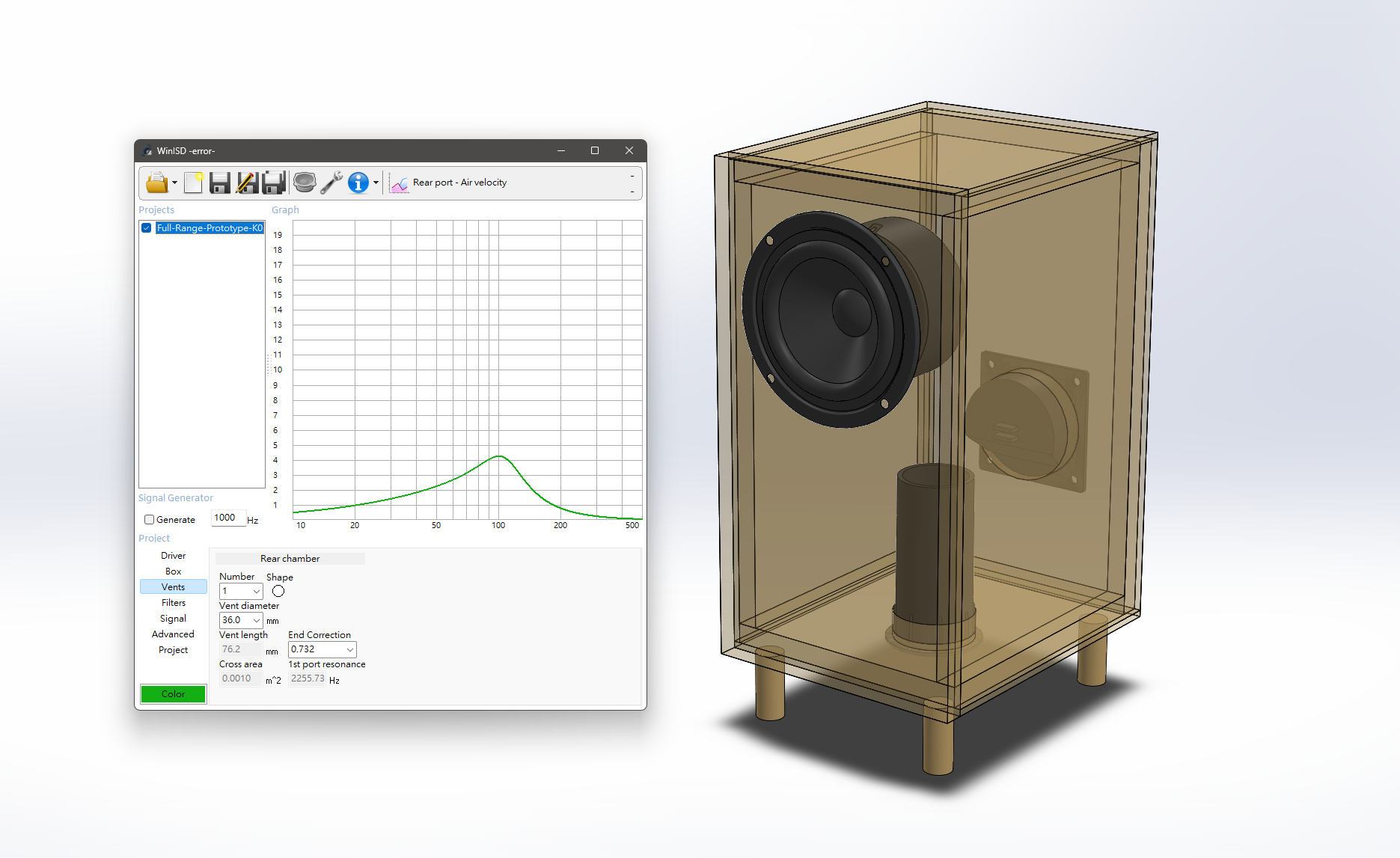
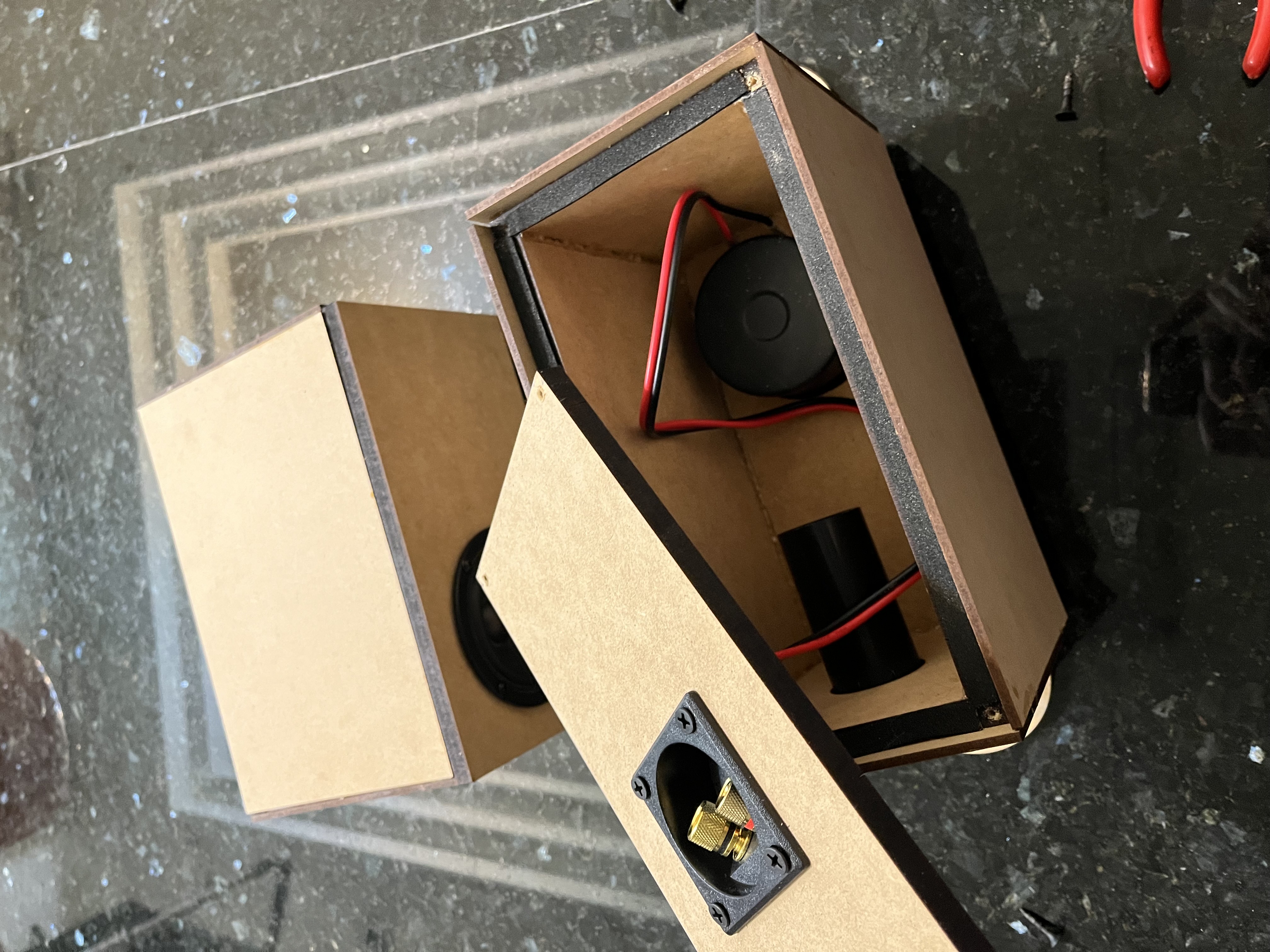
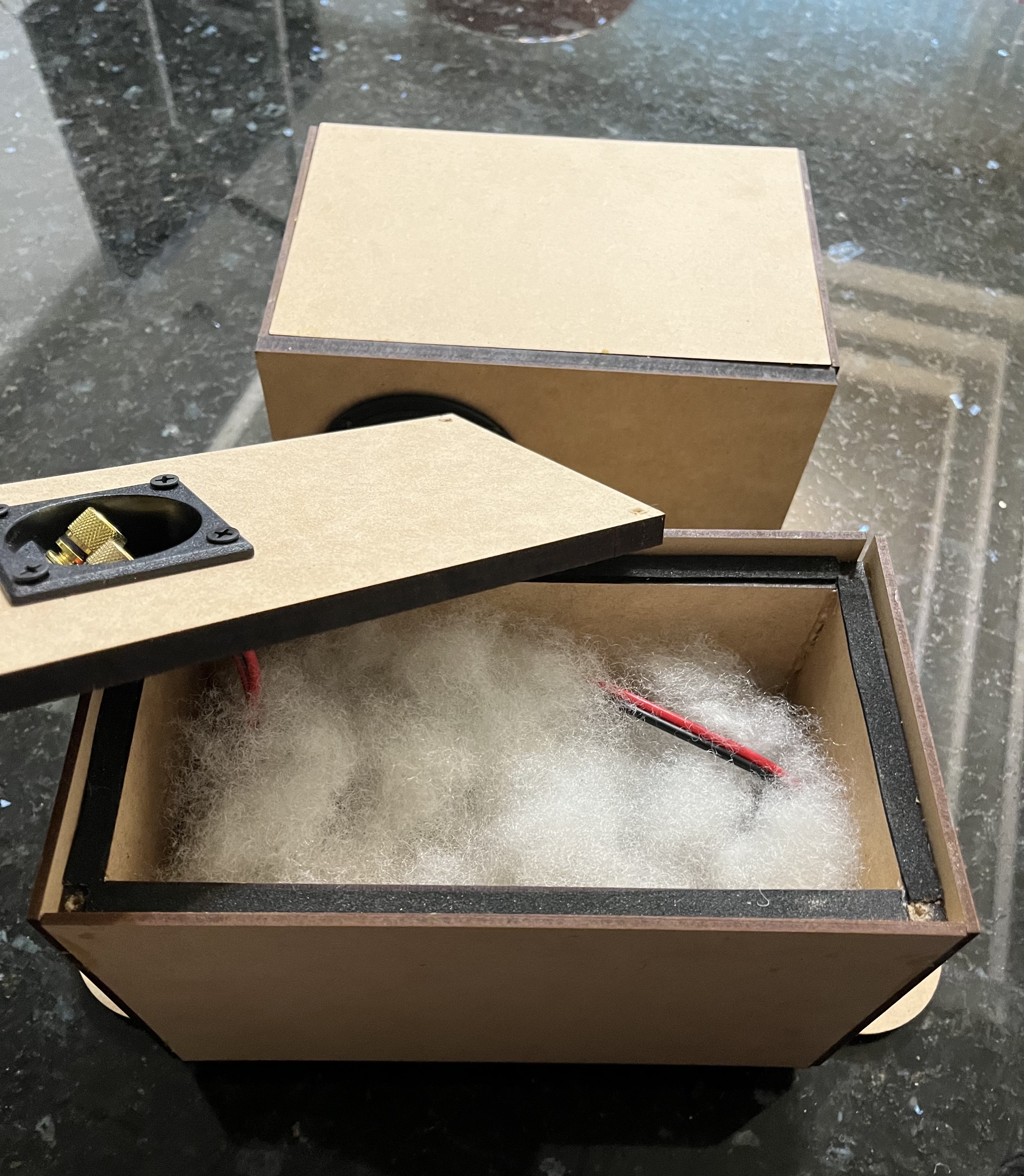
We purchased a pair of 3-inch full-range drivers with acoustic parameters provided by the supplier as our starting point. After referencing the research materials, we used WinISD for acoustic simulations of the enclosure, confirming the suitable enclosure volume and dimensions of the inverted tubes.
Subsequently, we used 3D modeling and MDF to fabricate the enclosures, along with procuring necessary components to realize our design.




Review
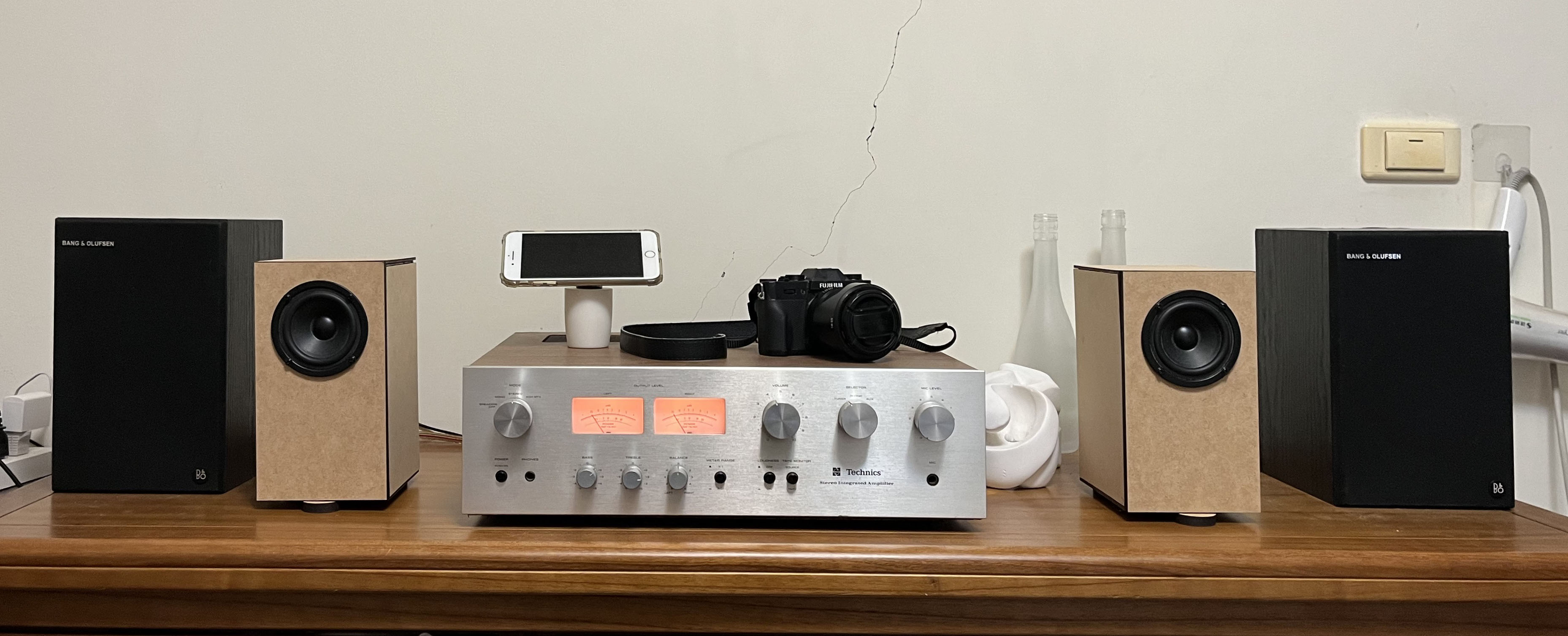
In evaluation, we compared our homemade speakers to existing B&O 2-way passive bookshelf speakers as a benchmark for listening experience (despite differing overall layouts). Our speakers demonstrated rich mid-range performance and detailed sound reproduction, though bass extension appeared relatively lacking, validating the reference value of our simulation data (rapid attenuation below 100Hz).
Overall, the sense of envelopment and soundstage performance was somewhat lacking. Nevertheless, for our first exploration into traditional acoustics and manufacturing speakers under limited equipment conditions, we are quite satisfied and look forward to further acoustic experiments in the future.
